According to the latest forecast from Semiconductor Intelligence, semiconductor capital expenditures (CapEx) will decrease by 14% in 2023, with the storage industry experiencing the largest reduction of 19%.
In recent years, the PC and smartphone markets have remained sluggish without any signs of improvement, and the storage industry has been severely affected. In addition to significant spending cuts by storage companies, contract manufacturers will also reduce capital expenditures by 11% in 2023, TSMC by 12%, UMC by 2%, and Gexin by 27%. IDM manufacturers have reduced their capital expenditures by 7%, with Intel planning to cut by 19%. Texas Instruments, STMicroelectronics, and Infineon have risen to the challenge and increased their capital expenditures in 2023, with the automotive and industrial related markets making the main contribution.
The decline in the personal computer market has affected Intel and memory companies, while the weakness in the smartphone market has affected TSMC and memory companies. Apple and Qualcomm are TSMC's two largest customers.
According to IC Insights, semiconductor capital expenditures increased by 35% in 2021 and 15% in 2022.
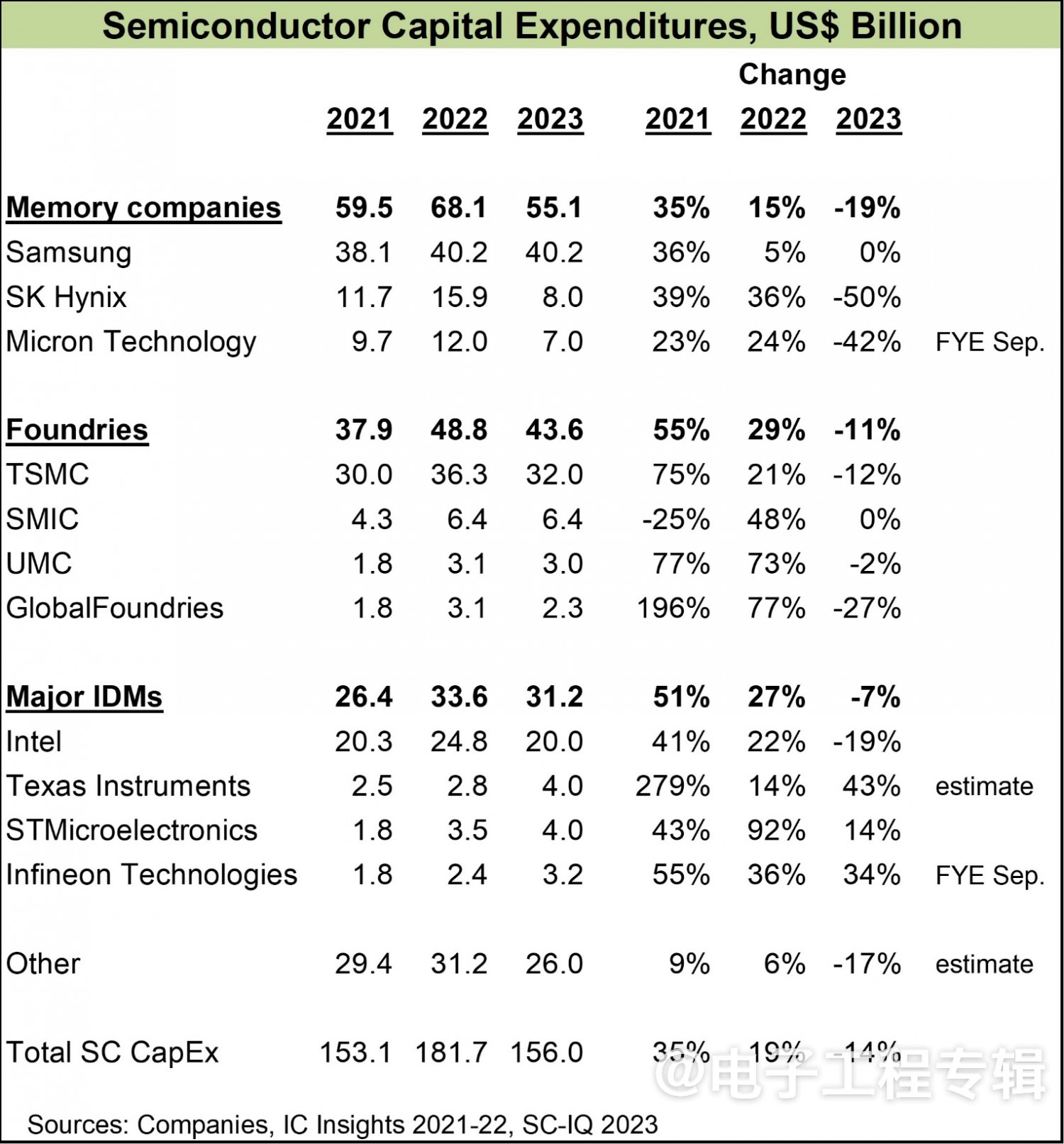
Figure 1: Semiconductor Capital Expenditure
The calculation formula for Capital Expenditure (CapEx) is: CAPEX=Strategic Investment+Rolling Investment. Capital investment expenditures refer to capital expenditures that need to be amortized over multiple accounting years for infrastructure construction, expansion of production, and other purposes.
The factors behind semiconductor capital expenditure decisions are complex. For example, the construction of a wafer fab takes two to three years to complete, and the estimated capital cost is $10 billion or even higher. To build a new wafer fab for a contract factory, it is necessary to predict the production capacity demand in the next few years in advance and plan the construction of the factory based on the customer's energy demand estimation. Contract factories account for about 30% of the total capital expenditure.
Storage giants suffer losses
The revenue performance of storage company giants Samsung, SK Hynix, and Micron Technology in South Korea has been plagued by a lack of demand.
In 2023, SK Hynix's capital expenditure will decrease by 50%, and Micron Technology's capital expenditure will decrease by 42%. Samsung only increased its capital expenditures by 5% in 2022 and is expected to maintain roughly the same level by 2023, reaching KRW 47.9 trillion last year.
Samsung announced revenue of KRW 63.75 trillion for Q1 2023, a decrease of 10% compared to the previous quarter. The Semiconductor and Device Solutions (DS) division had revenue of KRW 13.73 trillion, which was affected by weak storage demand, decreased utilization of wafer foundry capacity, and no improvement in customer orders and inventory adjustments.
SK Hynix's revenue in Q1 2023 was KRW 5.0881 trillion, with an operating loss of KRW 3.4023 trillion and a net loss of KRW 2.5855 trillion. The operating loss rate for Q1 2023 was 67%, with a net loss rate of 51%. Also affected by weak demand and falling product prices.
Omdia's latest research shows that in the semiconductor revenue of Q1 2023, Samsung was replaced by Intel and dropped to second place in the semiconductor sales ranking. In the quarter, Samsung fell 55.7% year-on-year, with revenue of $8.929 billion; Intel's revenue was $11.149 billion, a year-on-year decrease of 37.5%.
Last year, Samsung, SK Hynix, and Micron Technology were all within the top 5 in this ranking, but this year, except for Samsung, the other two have fallen out of the top ten. Storage companies are currently facing severe challenges, and the last time SK Hynix and Micron Technology did not make it into the top ten was in 2008.
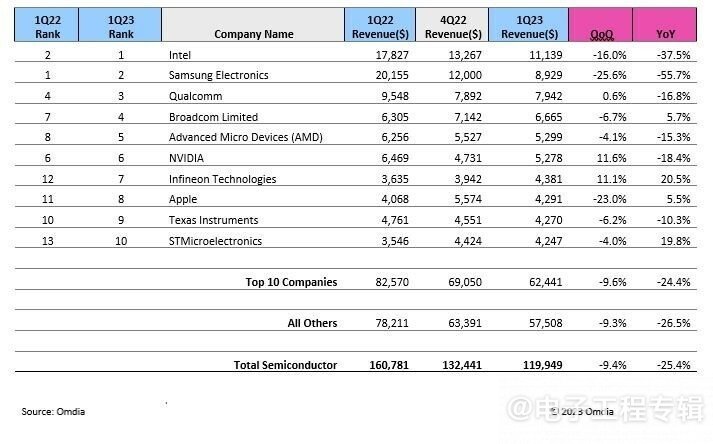
Figure 2: Top 10 global semiconductor sales companies in Q1 2023
Will 2023 be another major downturn year for the semiconductor market?
The capital danger threshold is a very important indicator obtained by reviewing historical cycles. When capital expenditures increase by more than 40%, it is usually predicted that there will be overcapacity and a decline in semiconductor growth in the future.
Why does Semiconductor Intelligence believe that 2023 will be another major downturn year for the semiconductor market.
From 1980 to present, the average percentage of semiconductor capital expenditure in the semiconductor market has been 23%, ranging from 12% to 34% on an annual basis, and from 18% to 29% on a five-year average basis.
The 5-year average of capital expenditures in the semiconductor market shows a cyclical trend.
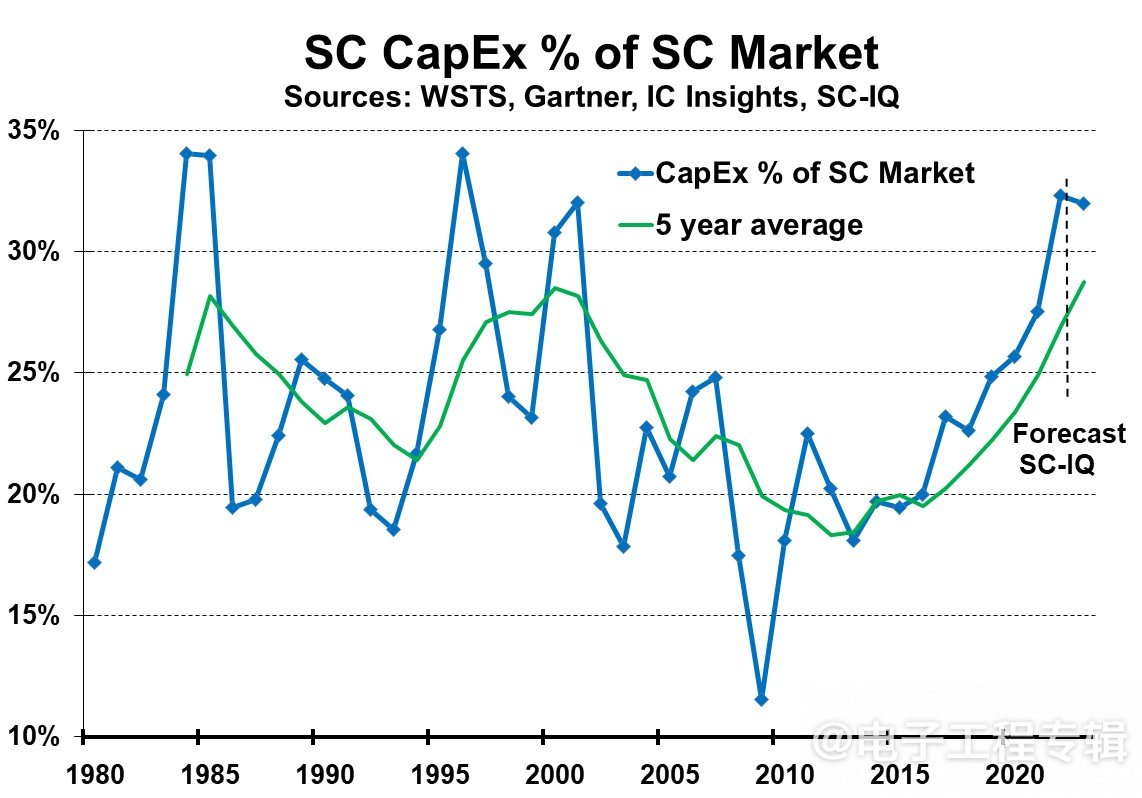
Figure 3: Average percentage of semiconductor capital expenditures to the semiconductor market (blue line), 5-year average of semiconductor capital expenditures to the semiconductor market (green line)
From Figure 3, it can be seen that the 5-year average of capital expenditure in the semiconductor market reached its maximum peak in 1985 and 2000, respectively. In 1985, the peak reached 28%, indicating that the semiconductor market had suffered a heavy blow; In the following 9 years, the average value decreased, began to rise in 1995, and recovered to a peak of 29% in 2000. In 2001, the semiconductor market experienced a significant decline. Subsequently, the average value decreased for 12 years, reaching a low of 18% in 2012, and then began to rise again, reaching a peak of 27% in 2022.
Semiconductor Intelligence predicts that the 5-year average will increase to 29% in 2023, and the semiconductor market will decline by 15%. Other institutions predict, such as Future Horizon?? NS believes that the semiconductor market will decline by 20%, while Gartner believes it will decline by 11.2%.
IC Insights data also shows that before 2019, there were four years in which IC shipments declined: 1985, 2001, 2009, and 2012. Among the four declines in IC unit shipments before 2019, two (1985 and 2001) occurred immediately after years of significant growth in IC shipments (followed by a decrease in shipments due to high inventory levels) - in 1984 and 2000, IC unit shipments showed high growth rates of 50% and 27%, respectively.
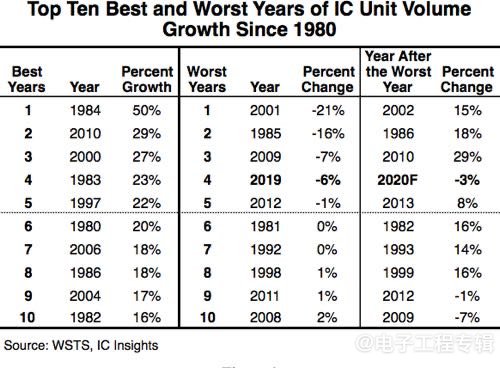
Figure 4: The best and worst decade of IC growth since 1980, sourced from WSTS and IC Insights
The high growth years of semiconductor capital expenditures are often the peak growth years of each cycle in the semiconductor market. From the annual changes in semiconductor capital expenditures and the semiconductor market, it can be seen that since 1984, the peak growth of the semiconductor market has matched the peak growth of capital expenditures. Any slowdown or decline in the semiconductor market within one or two years after the peak will lead to a corresponding decrease in capital expenditures。
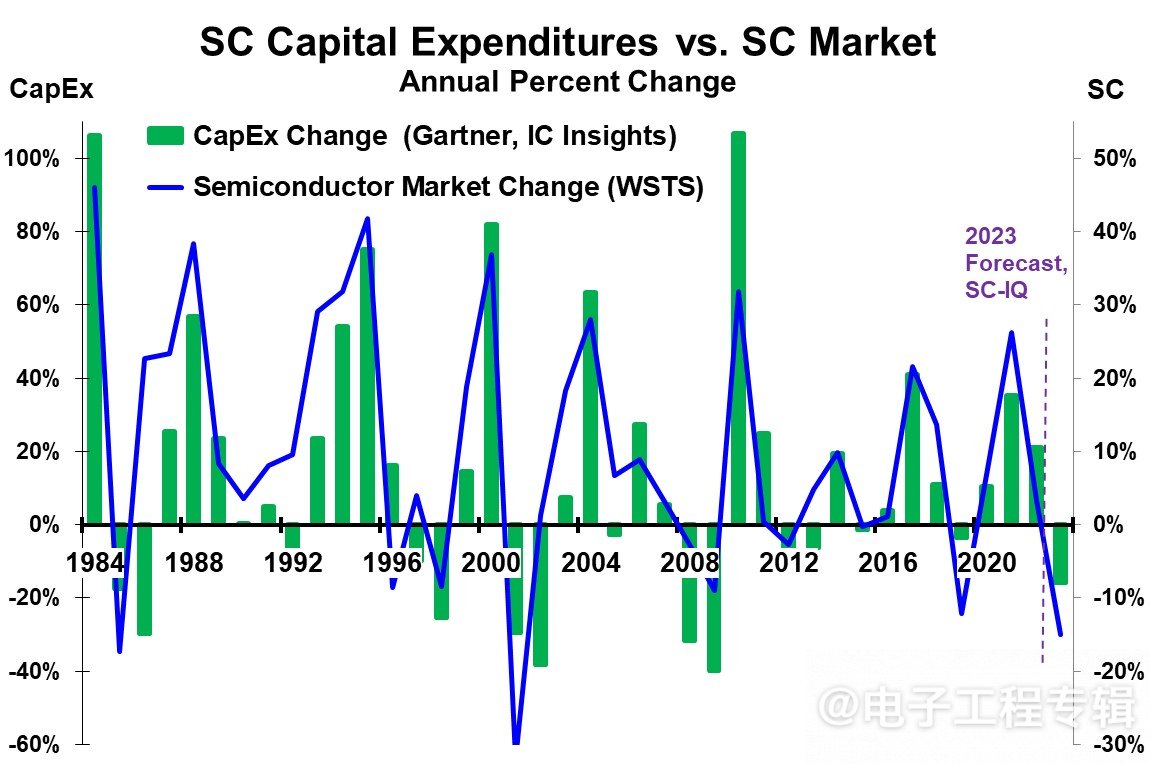
Figure 5: Relationship between semiconductor capital expenditures and the semiconductor market. The green bar on the left scale represents the annual changes in capital expenditures predicted from 1984 to 2023; The blue line on the right scale represents the annual changes in the semiconductor market.
However, 1988 was an exception, as capital expenditures did not decrease the following year and remained stable in the two years following the peak.
So there is a cycle in the semiconductor market, which exacerbates market volatility. In prosperous years, semiconductor companies, especially giants, will increase their capital expenditures to expand production capacity. In depressed years, they will correspondingly reduce capital expenditures, leading to IC overcapacity and product price declines after the prosperous period, exacerbating the market downturn.
Samsung has decided to maintain its capital expenditures at the same level as last year this year. The logical approach is to steadily increase capital expenditures annually based on long-term production capacity demand, but this decision is difficult to convince the company's shareholders to invest in capital during a recession.
In 2023, capital expenditures relative to the market will begin to decline again, and history suggests that this will be a possible outcome as a downturn in the semiconductor industry often slows down capital expenditures for companies.
The automotive industry: the main growth driver of the semiconductor market
As mentioned earlier, the capital expenditures of Texas Instruments, STMicroelectronics, and Infineon have risen to the challenge, with the automotive market being their biggest driving force.
Infineon, NXP, STMicroelectronics, Texas Instruments, and Renesas are the top 5 automotive semiconductor suppliers in sequence. In 2022, Infineon Automotive Semiconductor ranked first with a revenue of $8.1 billion, and its automotive business accounted for 47% of the company's total revenue; Renesas Electronics' automotive business revenue has increased from 17% to 43%, while NXP's automotive business accounts for 52% of total revenue.
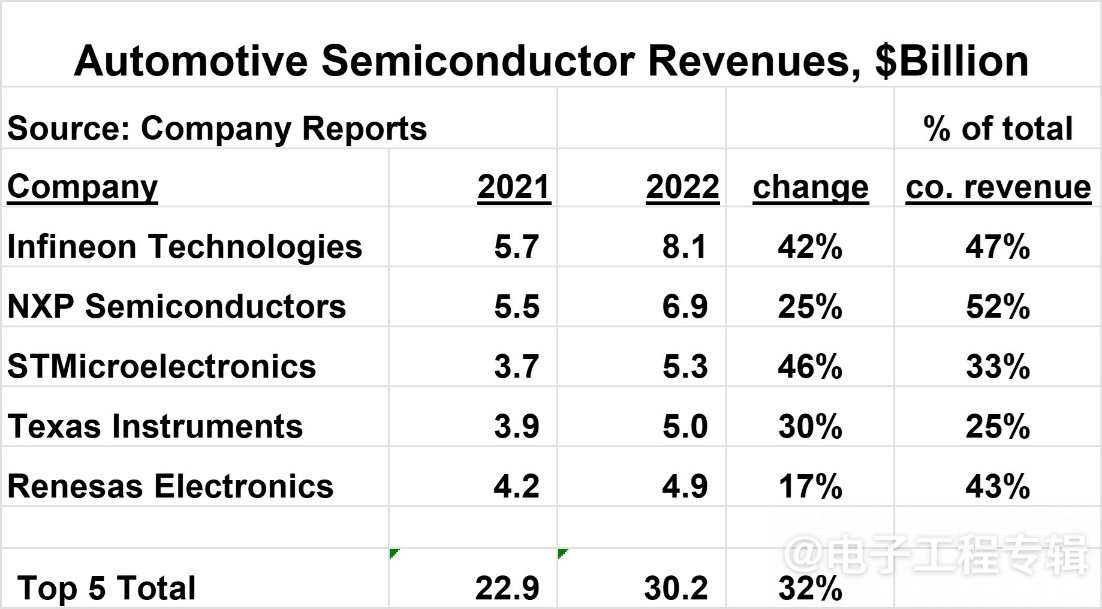
Figure 6: Top Five Global Sales Rankings for Automotive Semiconductors
STMicroelectronics' net revenue for Q1 2023 was $4.25 billion, with a gross profit margin of 49.7%, an operating profit margin of 28.3%, and a net profit of $1.04 billion. Jean Marc Chery, the President and CEO of the company, commented on the first quarter performance, stating that "revenue from automotive and industrial products exceeded expectations, while revenue from personal electronic product chips has declined." The company's sales revenue from automotive products and power discrete devices increased, with operating profit growing 145.3% year-on-year, totaling $577.4 million.
In February of this year, Texas Instruments planned to invest $11 billion to build a second 12 inch wafer fab in Lehi, Utah, with production starting as early as 2026. Texas Instruments' existing 12 inch wafer fab lineup includes DMOS6 in Dallas, Texas; RFAB1 and RFAB2 located in Richardson, Texas; And LFAB located in Lehi, Utah. Meanwhile, Texas Instruments is building four 12 inch semiconductor wafer fabs in Sherman, Texas.
In February of this year, Infineon was approved to invest 5 billion euros to build a semiconductor factory in Dresden, Germany. The factory will start production in 2026 and mainly produces power semiconductors and analog/mixed signal components that can be used in power supply systems, such as energy-saving charging systems, small car motor control units, data centers, and Internet of Things (IoT) applications.
In February last year, Infineon announced that it would spend over 2 billion euros to build a third factory in Kulin, Malaysia, for the production of silicon carbide and gallium nitride power semiconductor products. Renewable energy and electric vehicles are the main driving forces behind the sustained strong growth of the power semiconductor market.
In June of this year, STMicroelectronics and Sanan Optoelectronics jointly invested $3.2 billion to build a new 200mm silicon carbide device manufacturing plant in Chongqing, China, which will be put into operation in the fourth quarter of 2025.
In sharp contrast to other industries in the semiconductor market, the automotive semiconductor market is expected to show stable growth in 2023. Semiconductor Intelligence predicts a 14% growth in the automotive semiconductor market by 2023. The key factors driving this growth are:
Semiconductor suppliers have strong revenue and optimistic prospects for the first quarter of 2023;
The semiconductor shortage has eased to some extent, but there are still some shortages that will continue until the end of this year;
The inventory of automotive semiconductors is generally lower than expected;
The price of automotive semiconductors has increased;
An increase of 4% or more in automobile production;
The semiconductor content of each car continues to increase.
The average semiconductor content of future cars will continue to increase. Auto TechInsight predicted in January 2023 that the average semiconductor content per car will increase by 80% over the next seven years, from $854 in 2022 to $1542 in 2029.
More and more vehicles are adopting autonomous driving and assisted driving systems, including adaptive cruise control, lane keeping assistance, rearview video, and automatic emergency braking. These functions will increase the use of a large number of sensors and controllers.
There will also be a combination of car infotainment systems, which will provide navigation systems Wi-Fi、 The integration of smartphones, voice commands, audio, and video services will all drive the increase in automotive semiconductor content, making it the fastest-growing major field in the semiconductor market.
The sales of new energy vehicles are also showing an increasing trend. According to data released by the China Association of Automobile Manufacturers, in May 2023, the production and sales of new energy vehicles in China reached 713000 and 717000 respectively, an increase of 53% and 60.2% year-on-year, and the market share reached 30.1%. From January to May 2023, the production and sales of new energy vehicles reached 3.005 million and 2.94 million respectively, an increase of 45.1% and 46.8% year-on-year, with a market share of 27.7%.
A report by McKinsey&Company in April 2022 predicts a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.0% for the automotive semiconductor market and 6.8% for the entire semiconductor market starting from 2021. That is to say, the CAGR of automotive semiconductors is almost twice the growth rate of the entire semiconductor market.
This article is based on reports from Semiconductor Intelligence, Auto TechInsight, China Association of Automobile Manufacturers, McKinsey&Company, IC Insights, and others.









 Hot News
Hot News