The differences between glass passivation and acid-wash OJ processes for TVS transient suppression diodes?
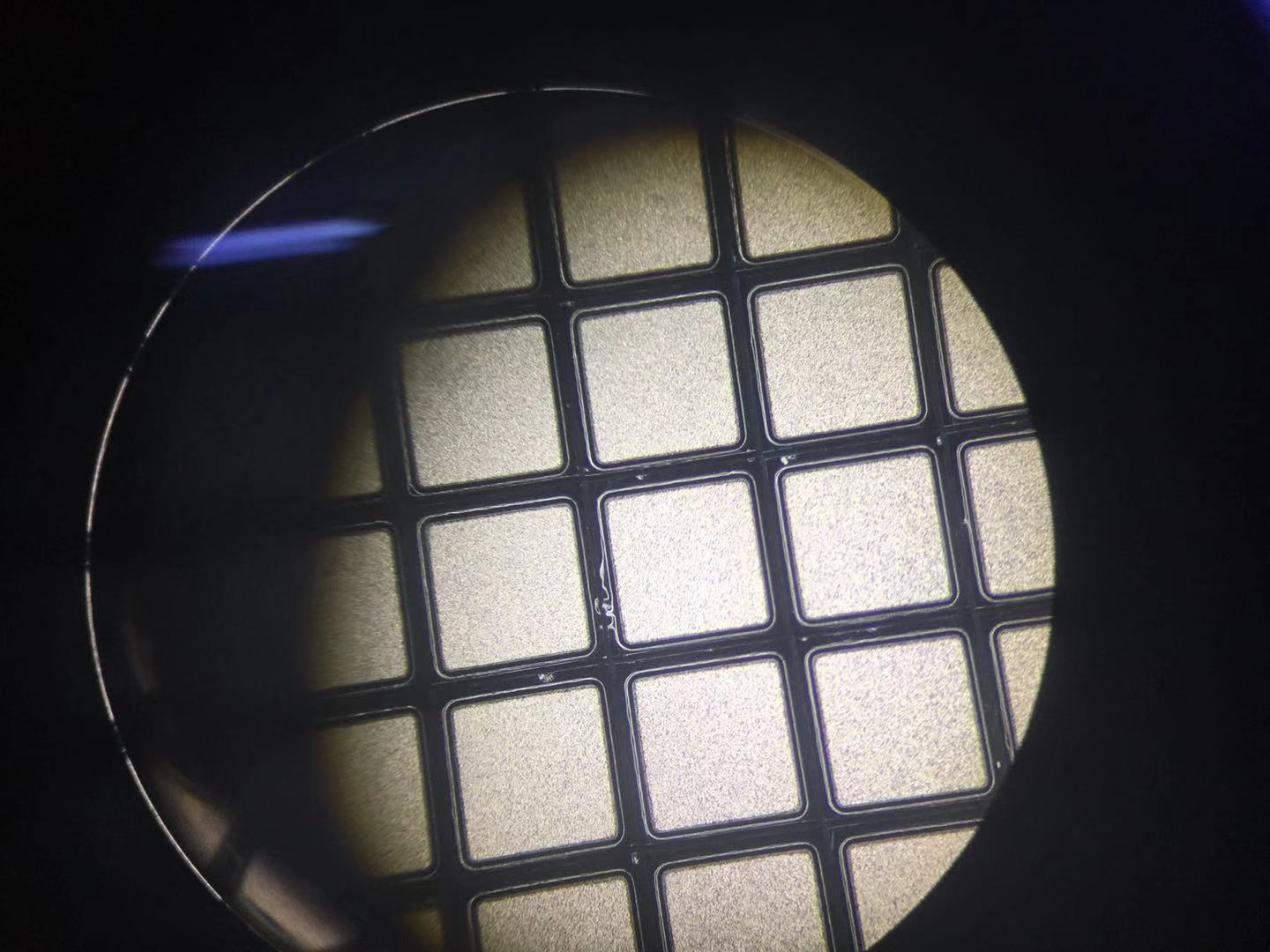
- Both glass passivation and acid-wash OJ processes are used to protect the PN junction surface of TVS diodes from oxidation and corrosion.
- TVS transient suppression diodes are typically made from silicon material due to its advantages, such as low leakage current and high voltage withstand capability. The voltage threshold can be adjusted by altering the doping concentration of the material.
- Glass passivation is a process that forms a glass film on the silicon surface to isolate it from oxygen in the air, preventing oxidation and corrosion. In contrast, the acid-wash OJ process is used to remove contaminants and oxide layers from the silicon surface. After encapsulation and die-bonding, a white adhesive coating (commonly known as "white encapsulation") is applied to the surface.
- Glass passivation uses glass powder sintering at temperatures above 800°C, offering high-temperature resistance and stable performance. However, the process is complex and less friendly to wafer dicing. Poor control may lead to chipping or hidden cracks, posing potential failure risks.
- The acid-wash OJ process has high requirements for adhesive properties, making it prone to bubble formation and environmental influence. For consumer-grade products, the probability of failure is generally acceptable to users.
Why is SiPos material added to PN junctions or dicing streets?
SiPos (Silicon Passivated) is a material used in the fabrication of TVS transient suppression diodes, typically formed on a SiO₂ (silicon dioxide) film.
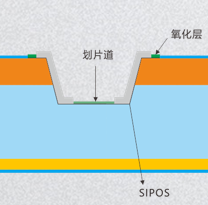
The addition of SiPos material primarily serves the following purposes:
- Protects the diode structure: The SiPos material covers the surface of the diode, forming a protective layer that prevents oxygen and other harmful substances from entering the diode interior, thereby reducing external corrosion and contamination.
- Improves electrical performance: SiPos material enhances the electrical characteristics of the diode, such as reducing reverse leakage current and increasing the threshold voltage.
- Enhances voltage withstand capability: SiPos material strengthens the diode's ability to withstand voltage, improving its overvoltage suppression performance.











 Hot News
Hot News