








As two leading giants in China's communications industry, ZTE and Huawei have achieved remarkable results in the 5G era, which is undeniable. Both tech giants have invested substantial human, material, and financial resources in 5G research. Following the announcements by China's three major telecom operators regarding the launch timeline for 5G smartphones, these two giants have also disclosed their commercial achievements in 5G. As the 5G era unfolds, the ultimate winner remains to be seen.
In the mobile communications sector, both Huawei and ZTE are frontrunners. Recently, ZTE announced its commercial achievements in 5G. According to the released data, ZTE has gradually recovered from the impact of U.S. sanctions, which posed a significant challenge. Fortunately, ZTE leveraged its accumulated strengths and secured 25 commercial 5G contracts, making it the communications provider with the second-highest number of 5G commercial contracts after Huawei. As the two major communications giants in China, the key difference between ZTE and Huawei lies in Huawei's substantial investment in communications technology R&D, which has positioned it as an industry leader in the field of communication technology.

Comparing China's two giants, Huawei and ZTE: which one is more impressive?
Both Huawei and ZTE are leaders in the communications field and are involved in the smartphone business. However, Huawei attracts more attention than ZTE, primarily due to their differing responses during the U.S.-China trade tensions. After the ZTE incident, ZTE adopted a cooperative approach to communicate with the U.S. government, ultimately resulting in a ruling that ZTE violated regulations and imposing hefty fines. In contrast, following the Huawei incident, Huawei took a firm stance, began utilizing its self-developed chips, and enhanced its global influence in 5G, among other actions. Huawei's response resonated more strongly with national pride and patriotic sentiment among the Chinese public.
From the perspective of patent achievements:
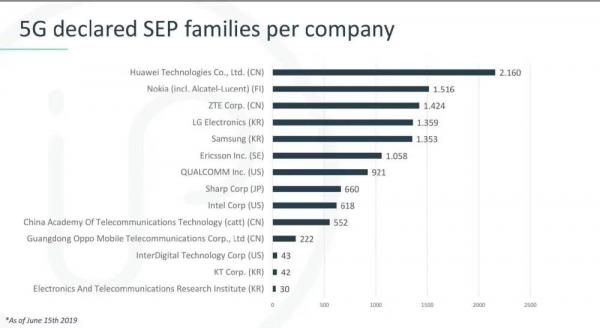
Data shows that ZTE has disclosed 1,424 families of 3GPP 5G standard-essential patents to the European Telecommunications Standards Institute, ranking among the top three globally. With over 3,500 5G patent applications, more than 30 of its experts hold key positions such as chairs and rapporteurs in major international standardization organizations. ZTE has submitted over 45,000 documents to international standardization organizations, including more than 7,000 proposals in critical areas like 5G air interface technology.
Huawei has contributed over 16,000 5G standard proposals, which, if printed on A4 paper, would stack nearly 10 meters high. In the global ranking of 5G standard-essential patents (SEPs), Huawei leads with 2,160 patents, accounting for 20% of the global total. In contrast, all U.S. companies combined hold less than 15% of 5G core patents.
Standard-essential patents (SEPs) refer to patents that are included in international, national, or industry standards and are indispensable for implementing those standards. When standardization organizations develop certain standards, some or all of the draft standards inevitably involve patents or patent applications due to technical or commercial necessity.
From the perspective of 5G commercial achievements:
As of the end of June, Huawei has secured 50 commercial 5G contracts globally and shipped over 150,000 sets of 5G equipment. These contracts span countries and regions including Spain, Ukraine, Austria, Germany, France, Switzerland, the United Kingdom, Turkey, Russia, Malta, Monaco, Latvia, Portugal, Lebanon, the United Arab Emirates, Oman, China (including Hong Kong), Indonesia, and Brazil.
To date, ZTE has obtained 25 commercial 5G contracts worldwide, covering major 5G markets such as China, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and the Middle East. The company collaborates with over 60 operators globally, including China Mobile, China Telecom, China Unicom, Orange (UK), Telefónica (Spain), WindTre (Italy), H3A (Austria), and Telkom Indonesia.
Beyond 5G patents and commercial contracts, 5G smartphones are undoubtedly a major focus of public anticipation. Currently, both ZTE and Huawei have launched their respective 5G smartphone models. Let's take a closer look.
Huawei Mate20X (5G) Smartphone:
According to Huawei, the Mate20X (5G) smartphone has received China's first 5G device network access license (identified as No. 001) and is set to launch in July. In terms of design, it features a 7.2-inch waterdrop display. For configuration, in addition to the Kirin 980 chipset, the device is equipped with the Balong 5000 5G multi-mode chipset. This is the world's first single-chip multi-mode 5G baseband, built on a 7nm process.

Notably, the Mate20X (5G) supports both 5G SA (Standalone) and NSA (Non-Standalone) network architectures, as well as 4G, 3G, and 2G networks. It is currently the only 5G dual-mode smartphone that supports both SA and NSA, and it also offers 5G and 4G dual SIM dual standby. This stands out as a significant advantage compared to 5G smartphones from other manufacturers.
ZTE Axon 10 Pro 5G Edition:
In terms of design, the ZTE Axon 10 Pro features a 6.47-inch AMOLED flexible display and supports HDR10+ high-definition video with a professional-grade video chip. For configuration, it is powered by the latest Qualcomm Snapdragon 855 mobile platform and supports the Sub6G frequency band, with downlink peak speeds of up to 2 Gbps. This provides consumers with an exceptionally smooth online video streaming and gaming experience. This smartphone is also expected to launch in July.

In conclusion, Huawei has shifted its focus to technological R&D. In the 5G field, Huawei indeed holds an edge over ZTE in various aspects of capability. Therefore, it is evident that Huawei can be considered a global leader in 5G. It is reported that in the second half of the year, major manufacturers will successively launch 5G smartphones, intensifying competition in the 5G landscape.
 Hot News
Hot News